There are a variety of Plastics available in market. The material properties varies very vastly from each other. Hence it is imperative to select correct material suitable to application. We always share our knowledge & experience to help customers choose the correct grade of material. Below mentioned are a few typical properties of popular plastic grades alongwith guide to application.
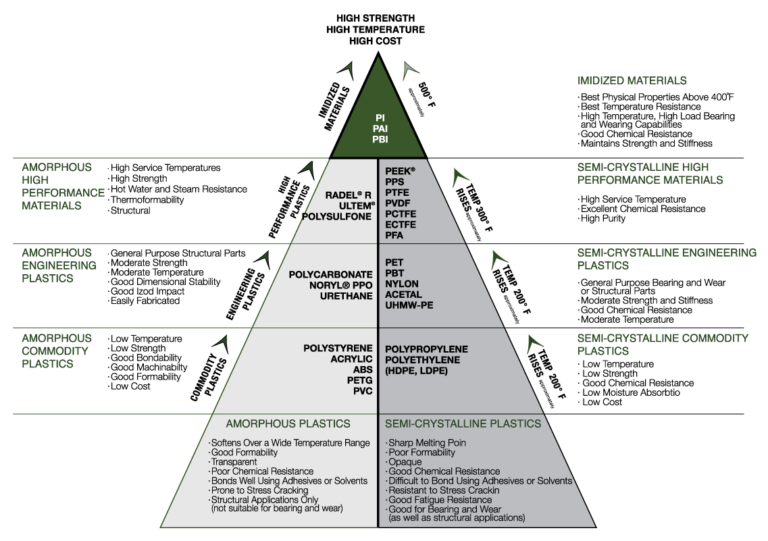
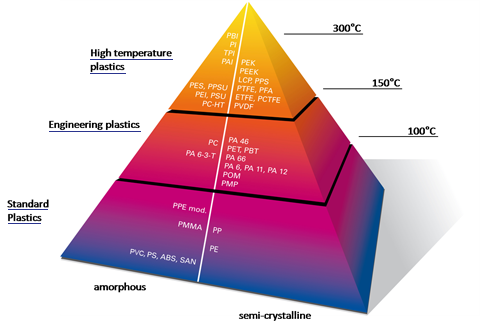
CLASSIFICATION OF PLASTICS:
There are three major groups in which majority of Plastics are generally classified as mentioned below:
AMORPHOUS THERMOPLASTICS:
Typical characteristics are as follows:
Good:
- They display good formability characteristics.
- Good Transperancy grades available
- They bond well using appropriate adhesives
Adverse:
- Soften over a wider Temperature range
- Poor Chemical Resistence
- Easily prone to Stress Cracking
USES:
Mainly Structural Applications only (Not for Wear/Bearing uses)
Major Popular Grades: ABS, PVS, Acrylic, Polycarbonate, Polystyrene (HIPS), PETG, Etc.
SEMI-CRYSTALLINE THERMOPLASTICS:
Typical characteristics are as follows:
Good:
- They have good chemical resistance characteristics.
- Resistant to Stress Cracking
- Good fatigue, Bearing & Wear Resistance
Adverse:
- They generally display poor formability properties
- They are opaque & are difficult to bond using adhesives.
- Easily prone to Stress Cracking
USES:
Major applications are for wear & bearing applications. Also suitable for structural applications.
Major Popular Grades:
Acetal, HDPE, LDPE, Nylon, PEEK, PET, Polypropelene, PTFE, UHMW-PE, Etc.
IMIDIZED MATERIAL:
Typical characteristics are as follows:
Good:
- They have very good chemical resistance characteristics.
- Good physical properties even above 200 Deg C.
- Good Bearing & Wear Resistance
Major Popular Grades:
PAI (Poly Amide – Imide) various grades.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Density of Specific Engineering Materials | ||
| SR | GRADE | DENSITY |
| PLASTICS | (GM/C.C.) | |
| 1 | Polyethylene, High-Density | 0.935 TO 0.960 |
| 2 | Polyethylene, Low-Density | 0.900 TO 0.925 |
| 3 | Polystyrene, High-Impact | 0.050 TO 0.500 |
| 4 | ABS | 0.050 TO 0.900 |
| 5 | Acetal (Delrin) | 0.400 TO 0.450 |
| 6 | Nylon, 66 | 0.400 TO 0.450 |
| 7 | Nylon 66, 40% glass | 0.440 TO 0.470 |
| 8 | Polycarbonate | 0.200 TO 0.250 |
| 9 | Polycarbonate, 30% glass | 0.430 TO 0.435 |
| 10 | PPO | 0.040 TO 0.070 |
| 11 | PPO, 30% glass | 0.280 TO 0.285 |
| 12 | Polyester teraphthalate | 0.700 TO 0.750 |
| 13 | 30% glass Polypropylene | 0.900 TO 0.925 |
| 14 | Polypropylene, 40% Talc | 0.260 TO 0.270 |
| THERMOSET PLASTICS | ||
| 15 | Carbon fiber, epoxy | 0.800 TO 0.850 |
| 16 | Fiberglass, epoxy | 0.900 TO 0.950 |
| 17 | Fiberglass, polyester | 0.900 TO 0.950 |
| 18 | Phenolics | 0.600 TO 0.650 |
| MATERIAL | UTS (Mpa) | Elongation in 50 mm (%) |
| ABS | 28-55 | 75-5 |
| ABS (reinforced) | 100 | – |
| Acetals | 55 – 70 | 75-25 |
| Acetals (reinforced) | 135 | |
| Acrylics | 40-75 | 50-5 |
| Cellulosics | 10-48 | 100-5 |
| Epoxies | 35-140 | 10-1 |
| Epoxies (reinforced) | 70-1400 | 4.2 |
| Fluorocarbons | 7-48 | 300-100 |
| Nylon | 55-83 | 200-60 |
| Nylon (reinforced) | 70-210 | 10-1 |
| PHENOLICS | 28-70 | 2-0 |
| POLYCARBONATES | 55-70 | 125-10 |
| POLYCARBONATES (reinforced) | 110 | 6-4 |
| Polyesters | 55 | 300-5 |
| Polyesters (reinforced) | 110-160 | 3-1 |
| Polyethylenes | 7-40 | 1000 – 15 |
| Polypropylenes | 20-35 | 500-10 |
| Polypropylenes (reinforced) | 40-100 | 4-2 |
| Polystyrenes | 14-83 | 60-1 |
| Polyvinyl Chloride | Jul-55 | 450-40 |
| Many Amorphous Polymers such as Acrylic & Polycarbonate do not have a specific melting point (T m), but rather they have a glass transition temperature (T g) | ||||
| MATERIAL | Tg (Deg C ) | Tm ( Deg C ) | ||
| ( GLASS – TRANSITION ) | MELTING TEMPERATURES ) | |||
| Nylon 6,6 | 57 | 265 | ||
| Polycarbonate | 150 | 265 | ||
| Polyester | 73 | 265 | ||
| Polyethylene | ||||
| High Densith | -90 | 137 | ||
| Low Densith | -110 | 115 | ||
| Polymethylmethacrylate | 105 | – | ||
| Polpropylene | -14 | 176 | ||
| Polystyrene | 100 | 239 | ||
| Polytetrafluoroethylene ( Teflon ) | -90 | 327 | ||
| Polyvinyl Chloride | 87 | 212 | ||
| Rubber | -73 | – | ||
| DESIGN REQUIREMENT | TYPICAL APPLICATIONS | PLASTICS |
| Mechanical Strength | Gears, cams, rollers, valves, fan blades, impellers, pistons. | Acetals, nylon- Phenolics, polycarbonates, Polyesters, Polypropylenes, epoxies, polyimides, |
| Wear resistence | Gears, Wear Strips and liners, bear-ings, bushings, roller-skate Wheels. | Acetals, nylon- Phenolics, polyimides, polyurethane, ultrahigh- molecular- weight Polyethylene. |
| Frictional Properties | ||
| High | Tires, nonskid surfaces, footware, Flooring | Elastomers, rubbers. |
| Low | Sliding surfaces, artificial joints. | Fluorocarbons,polyesters, Polyethylene, Polyimides. |
| Electrical resistance | All types of electrical Components and equipment, appliances, electrical Fixtures. | Polymethylmethacrylate, ABS, FLUOROCARBONS,NYLON,polyarbonate, polester, polypropylenes, ureas,phenolics, silicones, rubbers, |
| Chemical resistance | Containers for Chemicals, laboratory equipment, components for Chemical industry, food and beverage containers. | Acetals, ABS epoxies, polmethylmethacry-late, fluorocarbons, nylon, Polycarbonate,Polyester, polypropylene, ureas, silicones, |
| Heat resistance | Appliances, cookware, electrical components. | Fluorocarbons, Polyimides silicones, acetals, Polysulfones, phenolics, epoxies. |
| Functional and decorative features | Handles, knobs, camera and battery cases, trim moldings, pipe fittings. | ABS acrylics, cellulosics, phenolics, polyethylenes, polpropylenes, polystyrenes, polyvinyl Choride. |
| Functional and transparent features | Lenses, goggles, safety glazing, signs,food-processing eqnipment | Acrylics, Polcarbonates, Polystyrenes, polysnlfones, laboratory hardware, |
| Housings and hollow Shapes | Power tools, bousings, sport helmets, telephone cases. | Abs, cellulosics, phenolics, polycarbonates, polyethylenes, polypropylene, polystyrenes. |